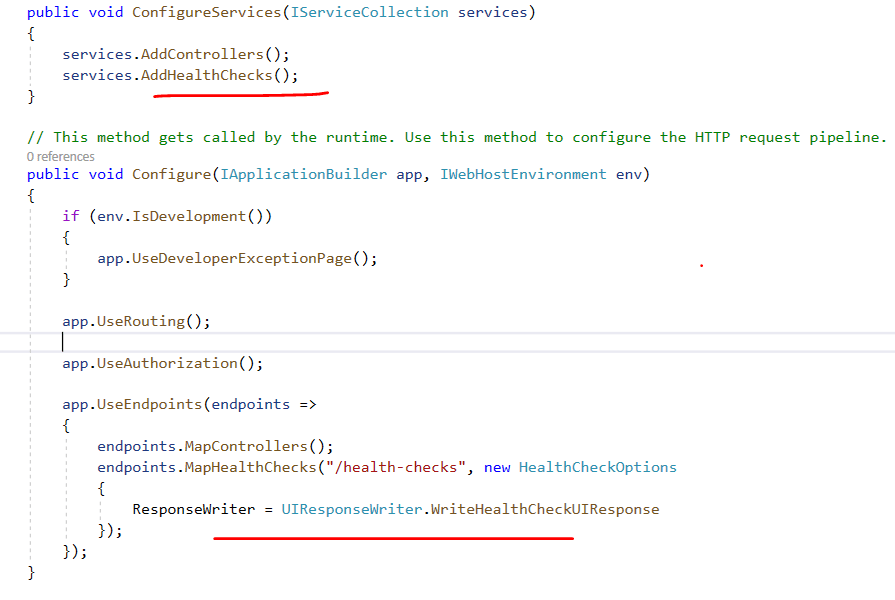
I have seen people get confused when using yield
I will give a simple example
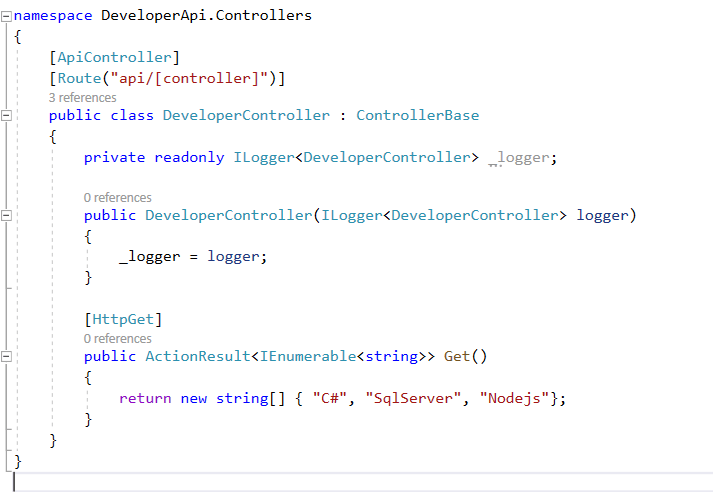
In our app, we are getting list of 50,000 employee details and printing them
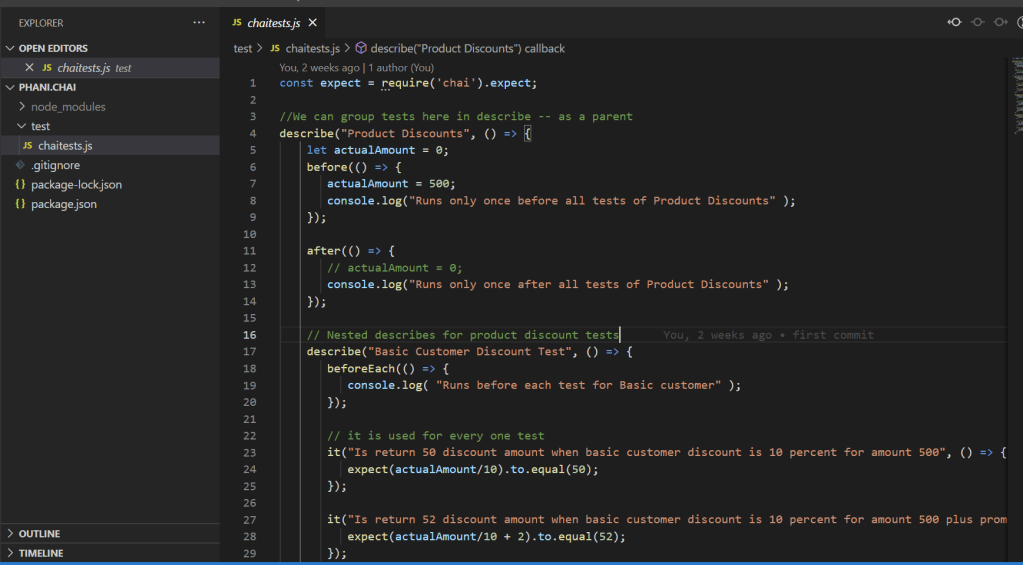
Usually without yield, the code looks like
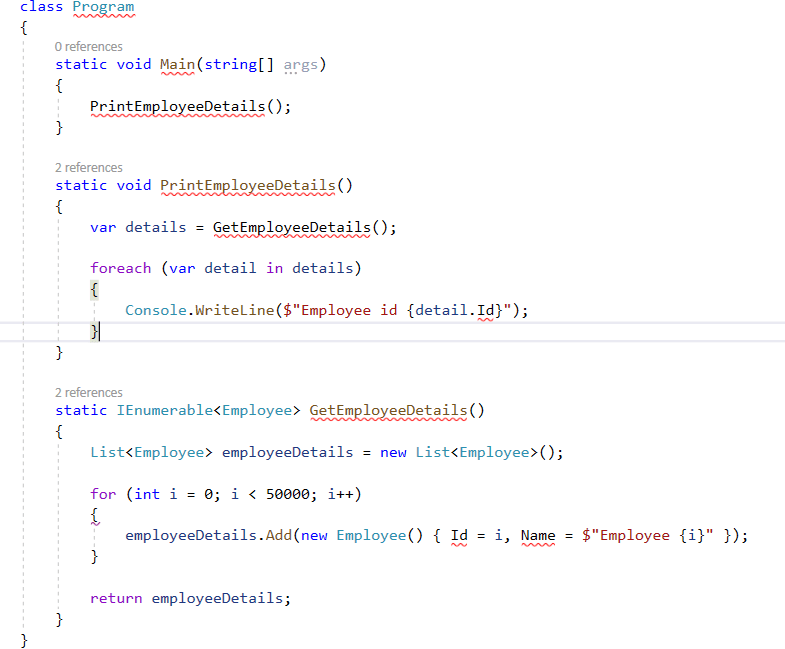
Here, we are getting list of 50,000 records which we can assume they are getting from api or from db.
Looping through the details and printing them
If we have lots of records, and iterating them will be a heavy process and affects memory usage and performance
One of the simple way is to use yield return to handle these type of situtations
The only change we do is remove list of details to return and just return only single yield return in for loop
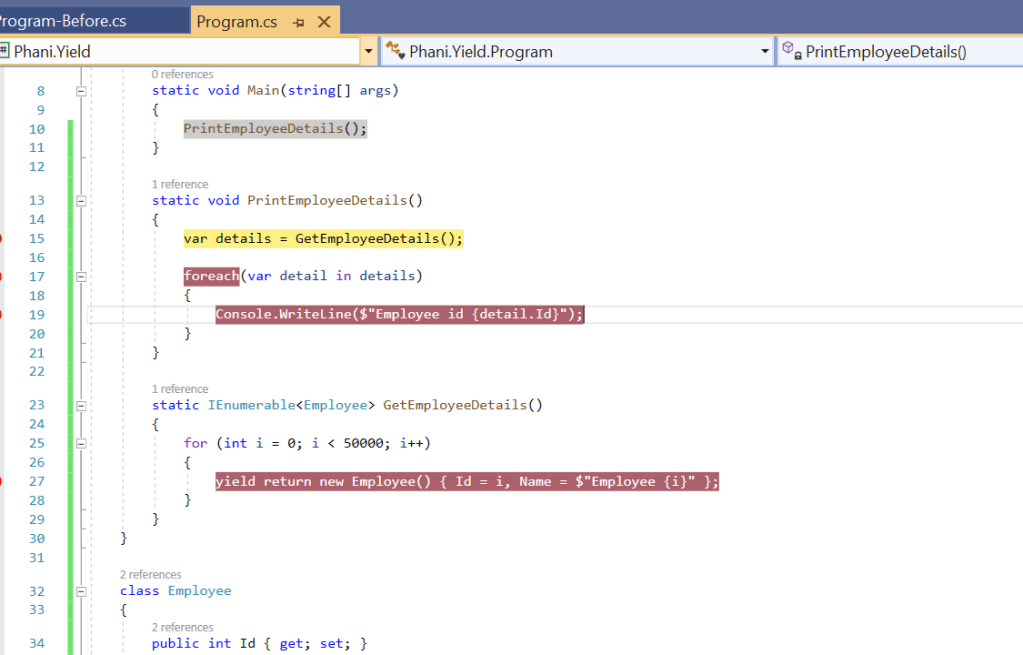
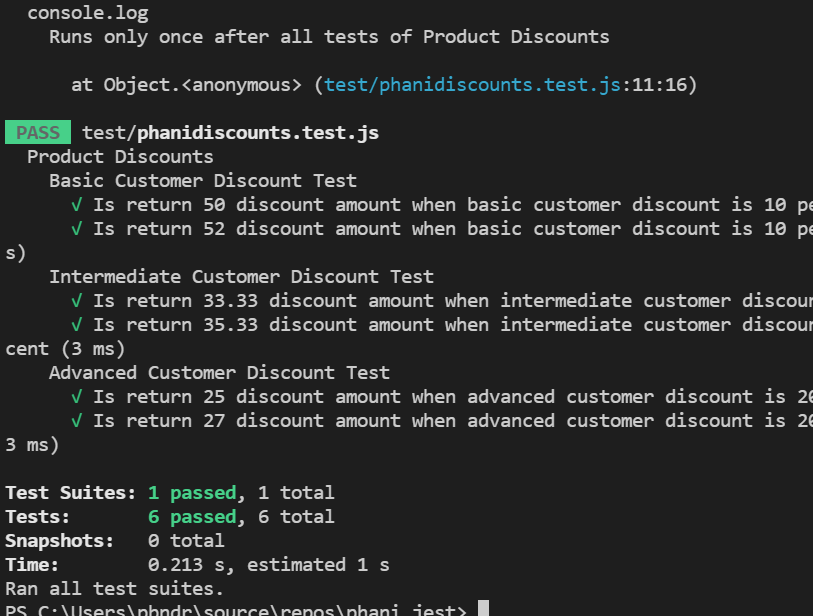
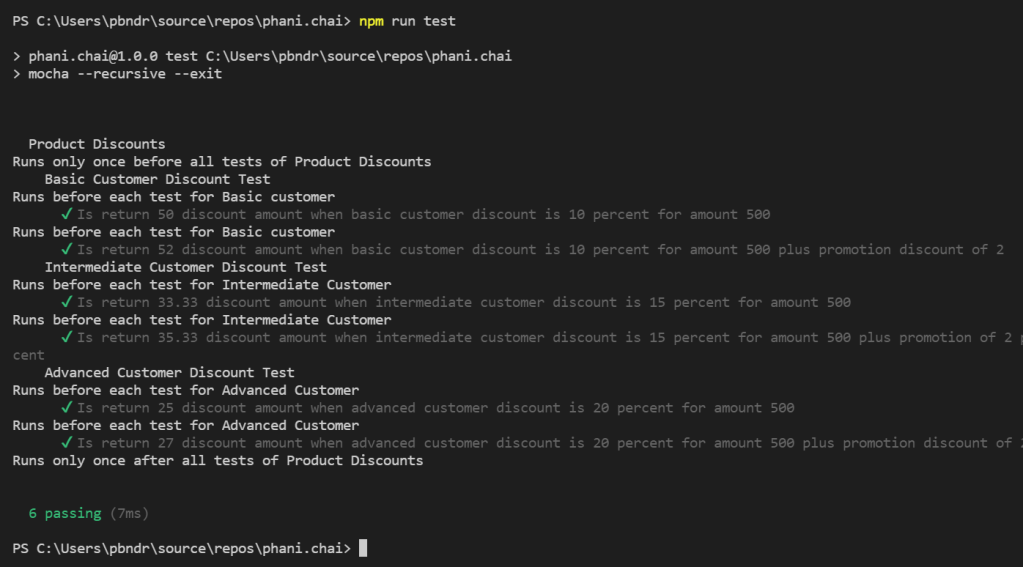
Lets debug and see the results
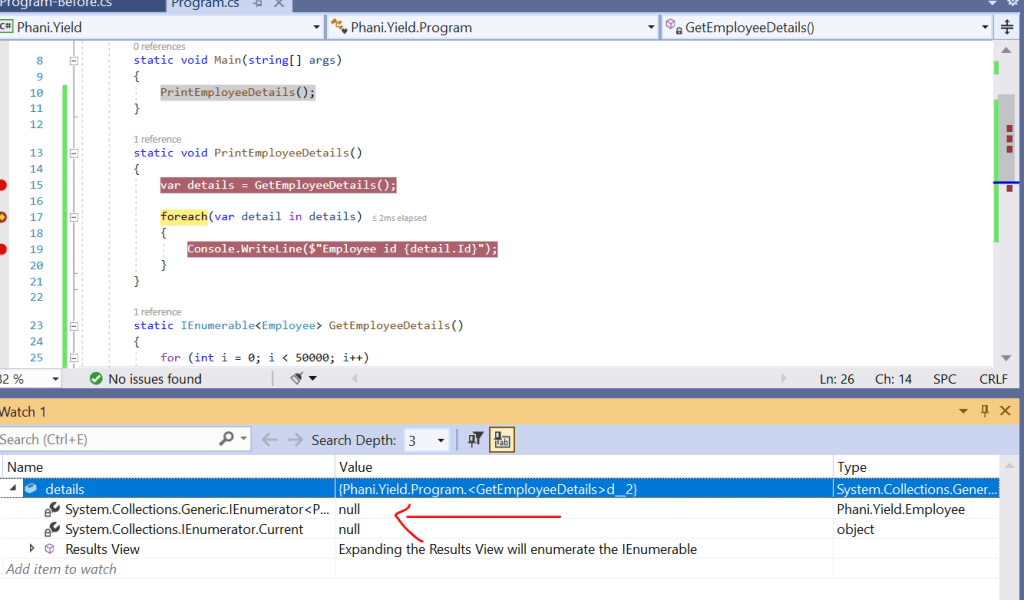
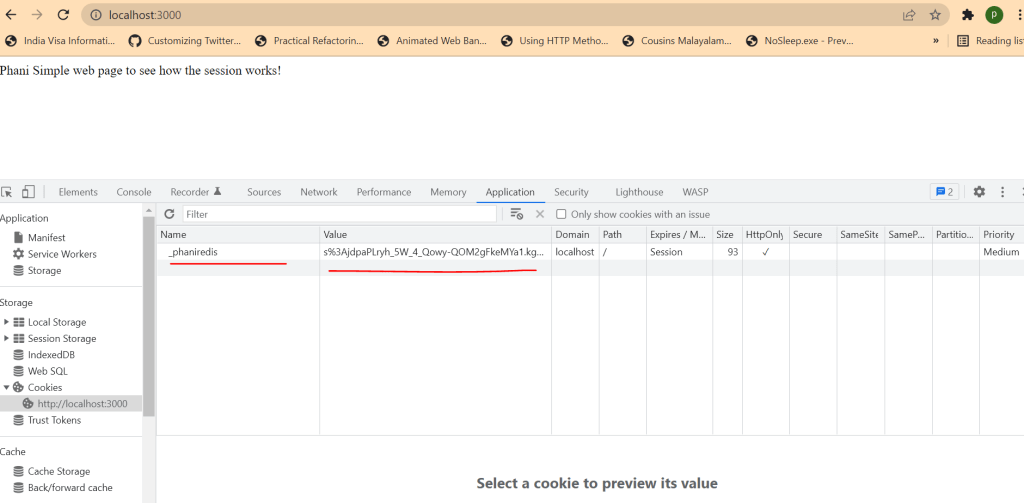
Here in watch window, you can see the details is empty. which doesnt have 50,000 records.
When looping through we get the single record and only stores single item in memory .
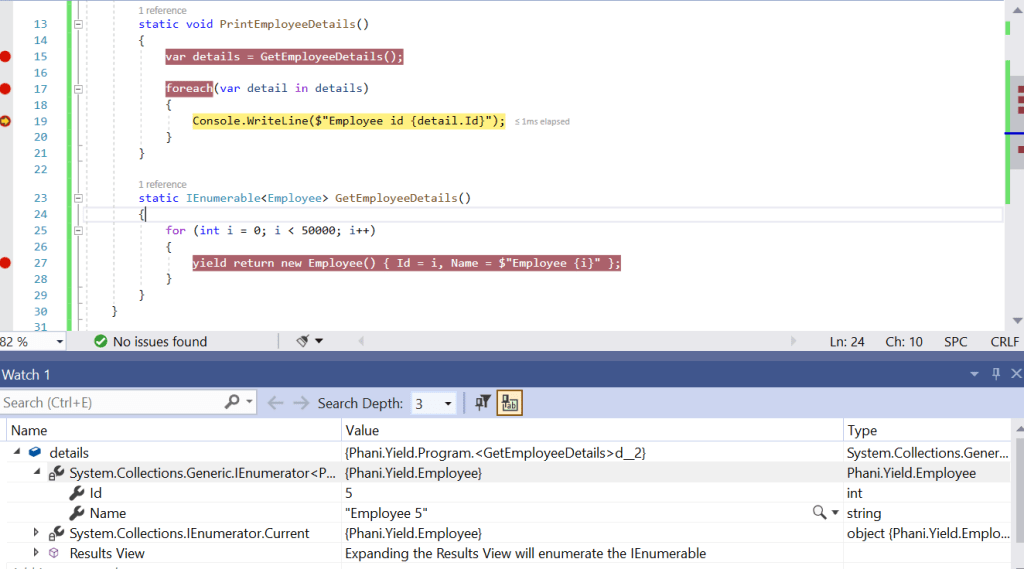
Now, i looped 5 times and you can see details object will have only one record. so it doesnt matter how many records the list will have.
Code in my Github: https://github.com/pbndru/Phani.Yield