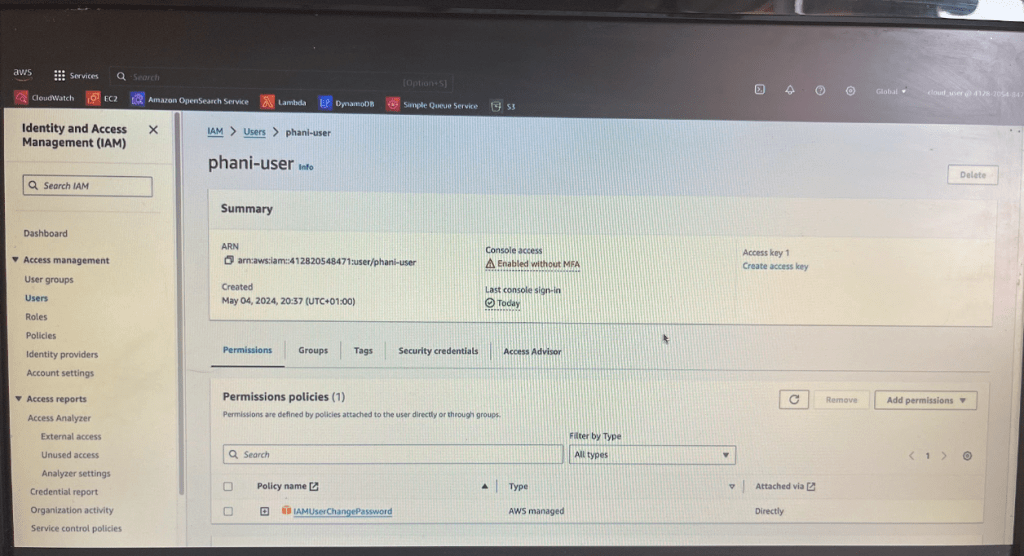
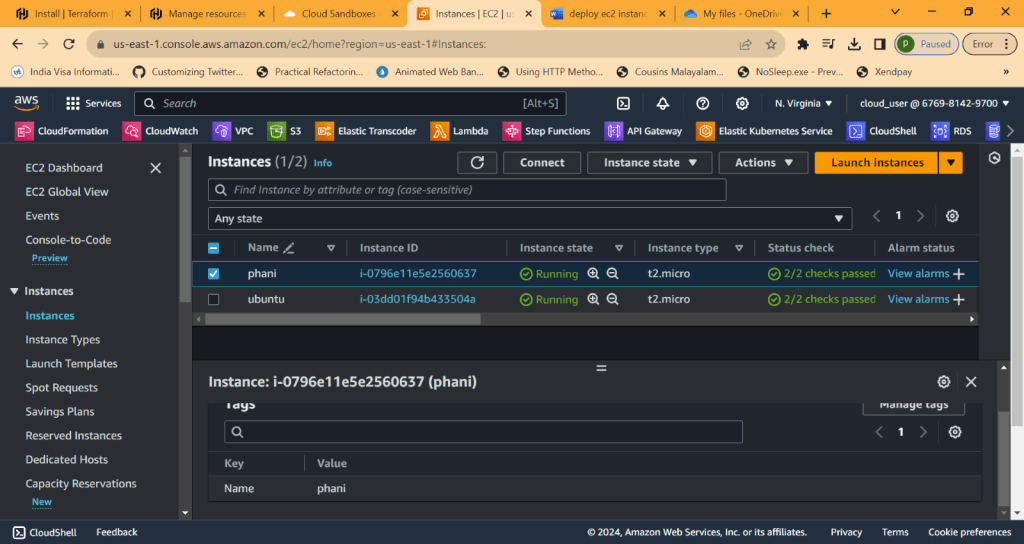
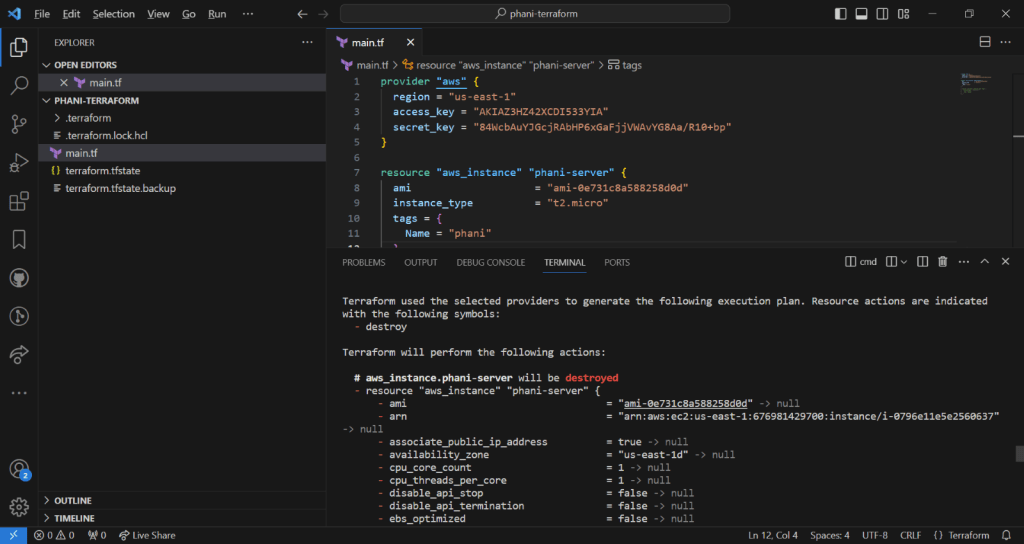
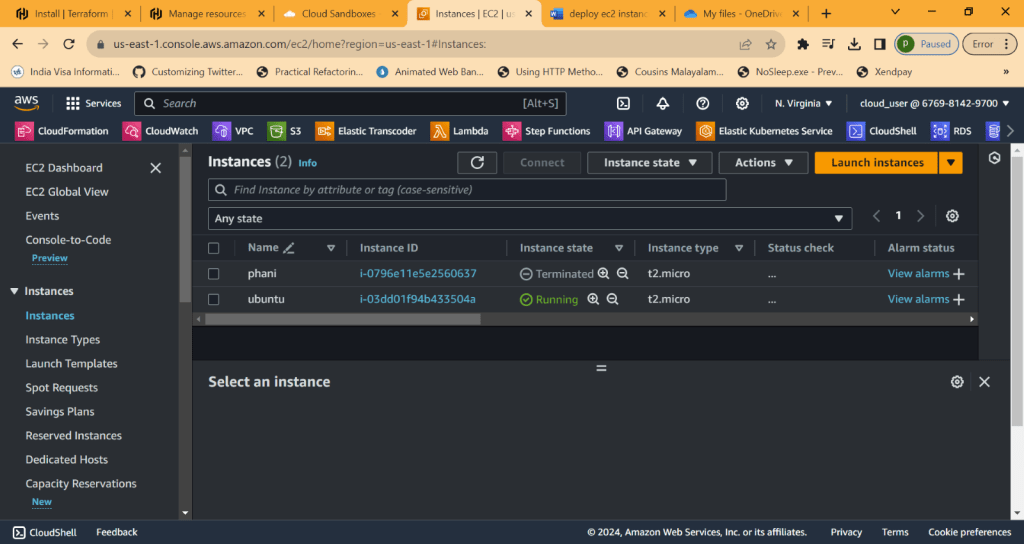
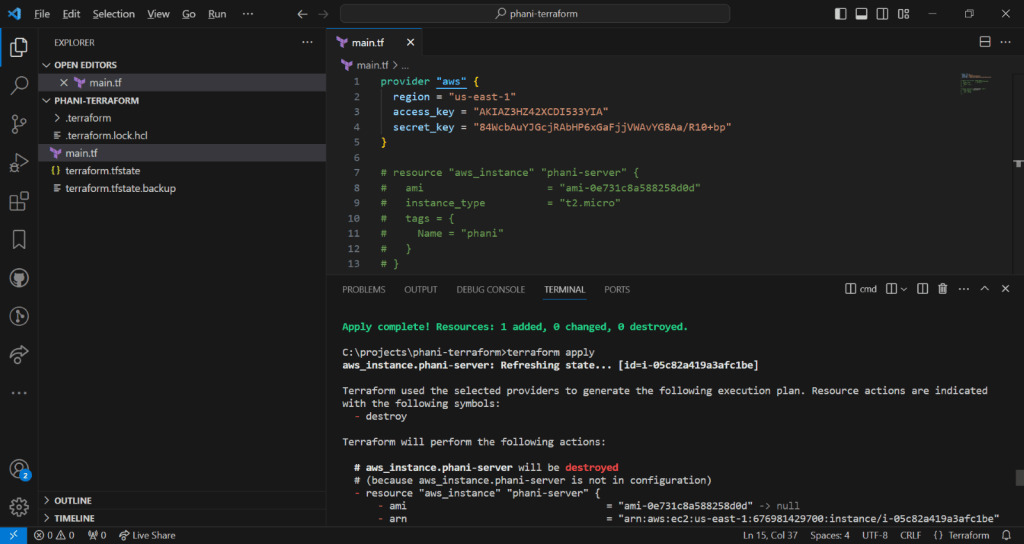
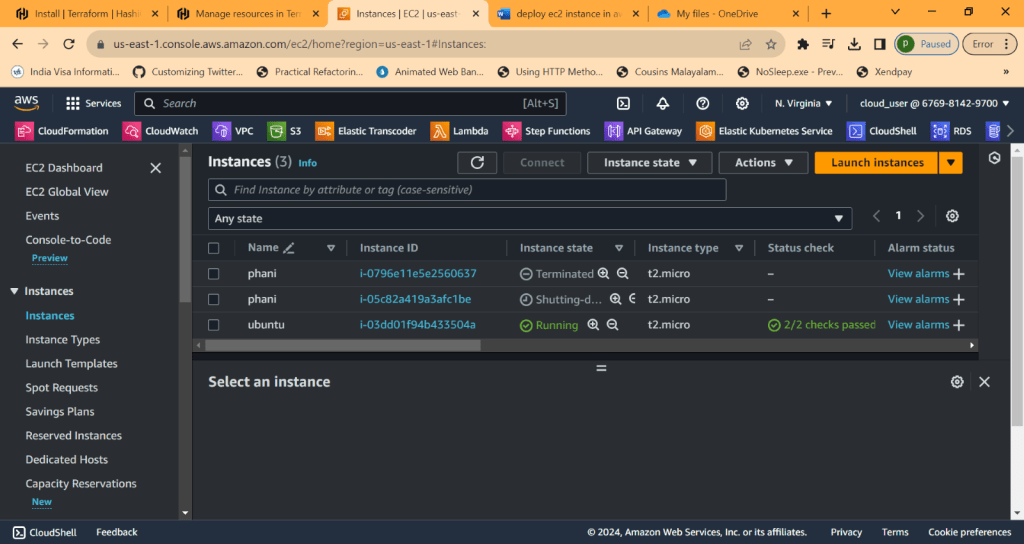
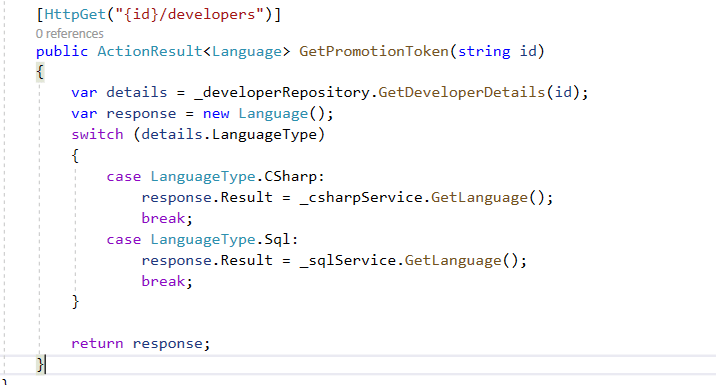
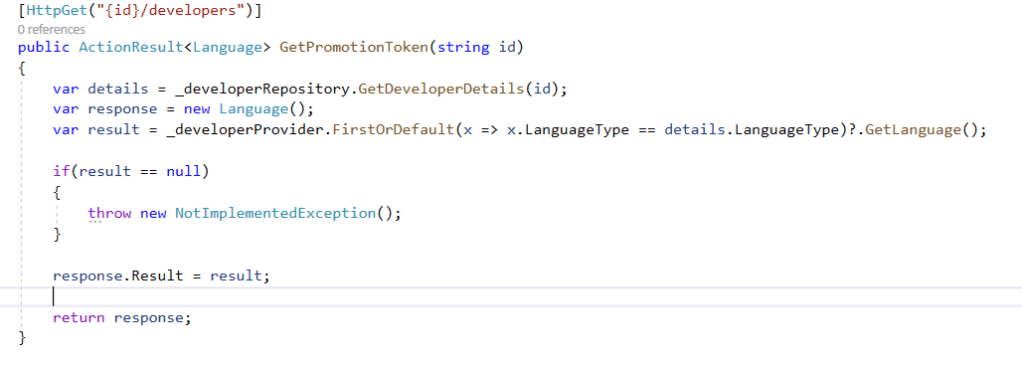
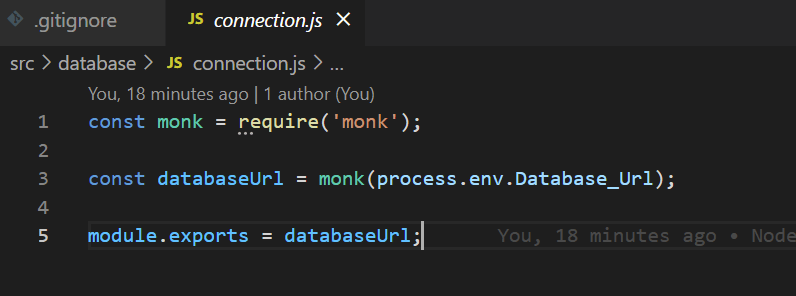
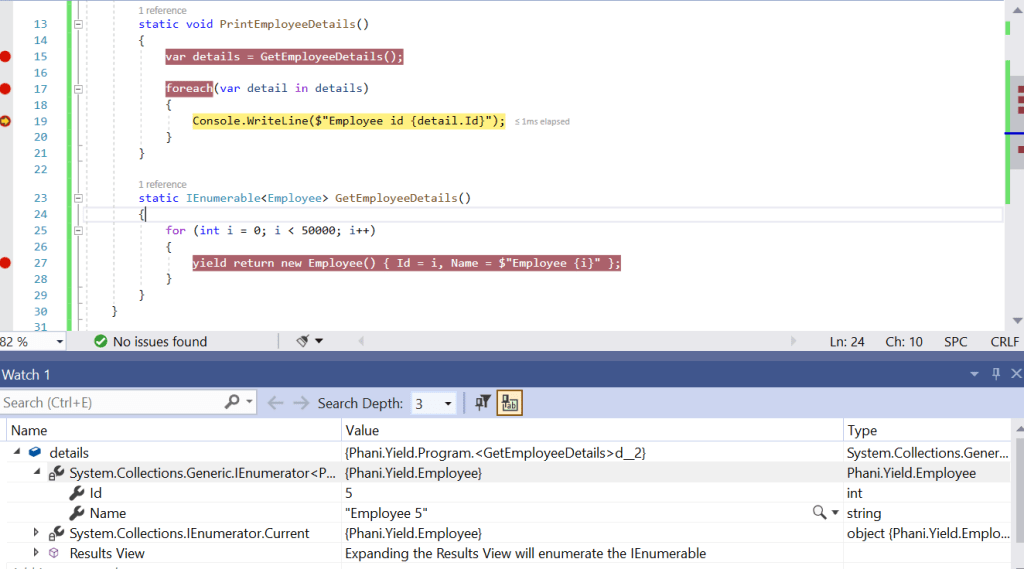
EC2 represents Elastic Cloud compute
Ec2 instance is about you are requesting AWS to provide you a virtual server
Example:
An application requires huge storage. So depending upon that you will choose which type of ec2 instance is required. There are many types of ec2 instances available like General , Compute optimised, memory , storage, accelerated.
Now lets use general ec2 type instance
You can create Ec2 instance through the UI or through the CLI where you need to just select instance type and AWS will give you that instance type and AWS will also charge you accordingly
We also need to know concept of regions and availability zones which will come here
You will create ec2 instance that is very close to your client location. Inside each region you have multiple availability zones as well
If there was a disaster recovery like short circuit or for some reason the region went down. To avoid this problem what AWS suggests is within a region we will have multiple availability zones.
For example if you have selected a region called London, then AWS says that we have availabilities on in North west and North east of London
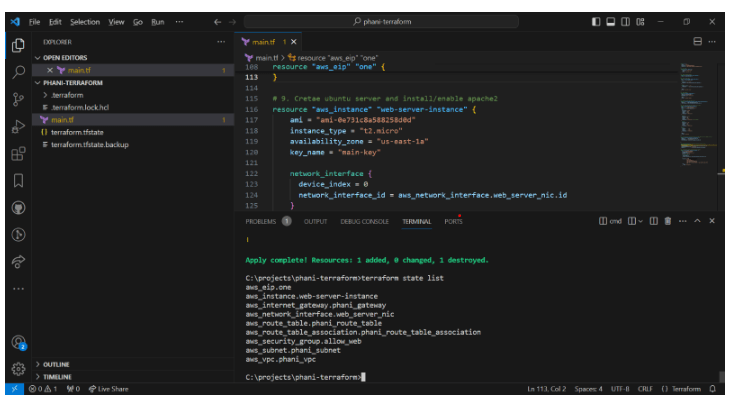
Now lets go to Ec2 instances and click on launch on instance
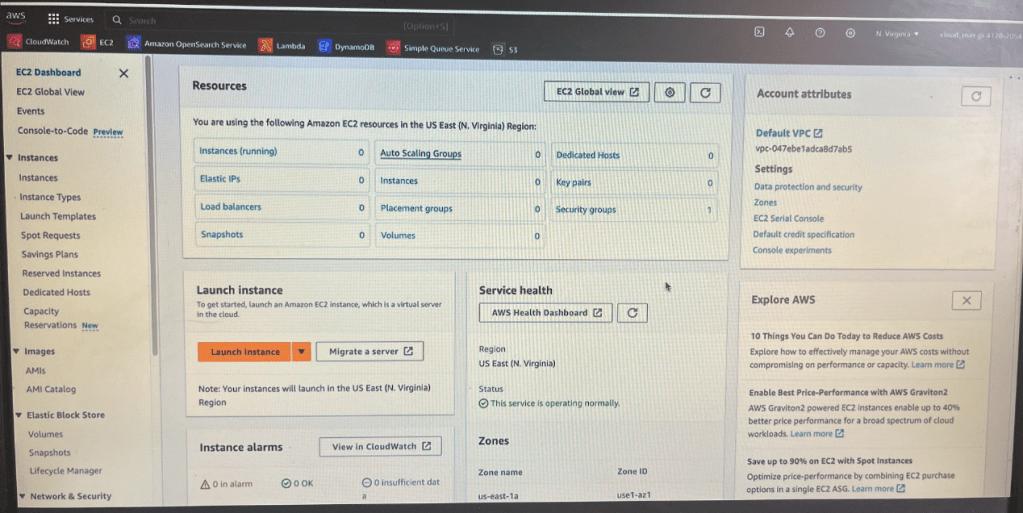
lets create phani-e2 instance. By default you have all of these operating systems
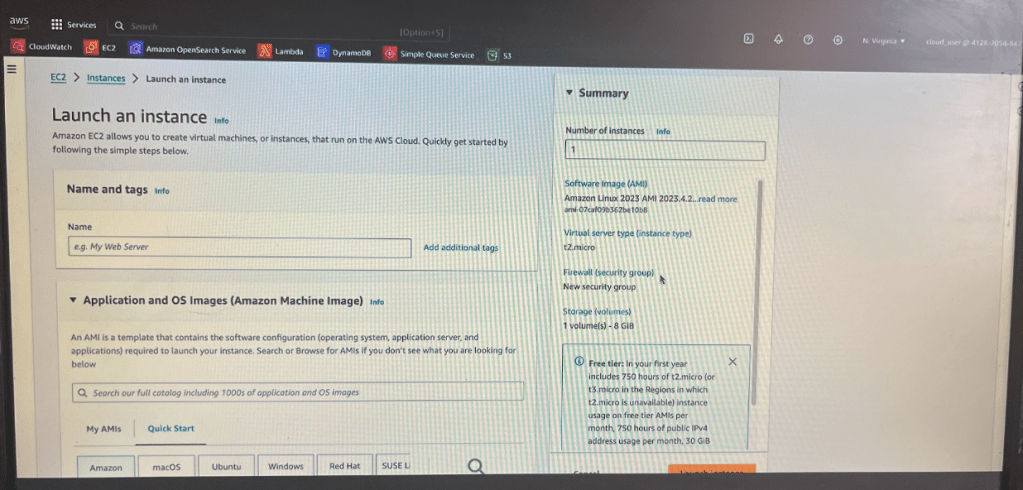
Lets select ubuntu server and select a version. I selected free -tier as if anything else aws willl charge me
Authentication to the instance is disabled by default. The only way you can log into the instance is using key value pair.
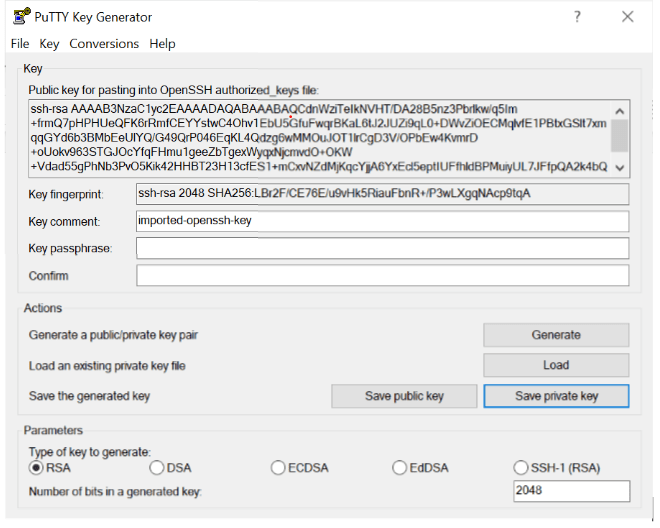
key value pair is nothing but a combination of public private key which you use to log into the instance
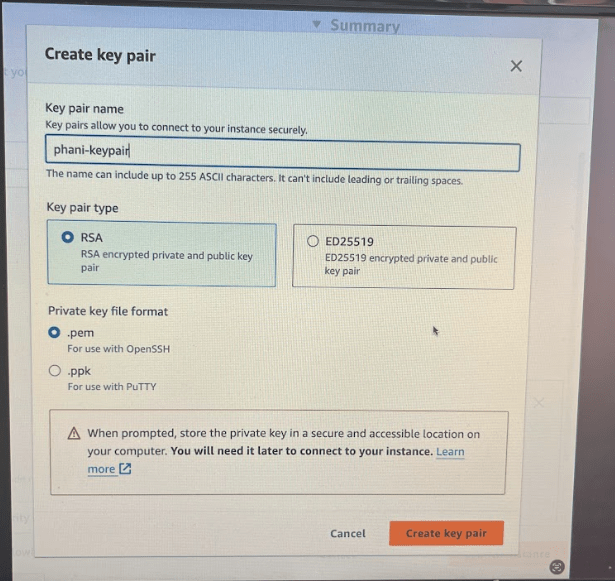
Lets create key pair. Here i create phani-keypair with .pem file format and store that file somewhere. here i stored in downloads folder
Lets ignore storage and networking for now.
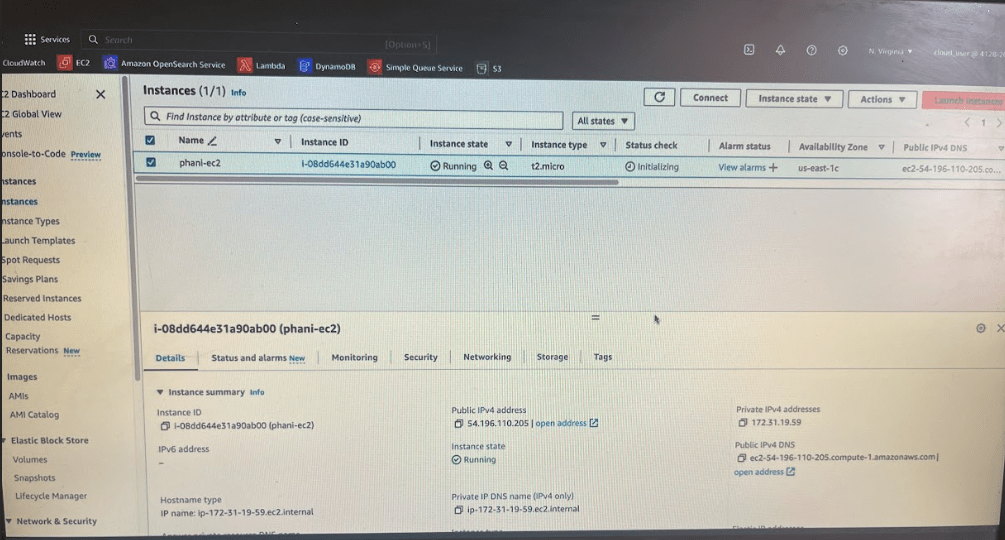
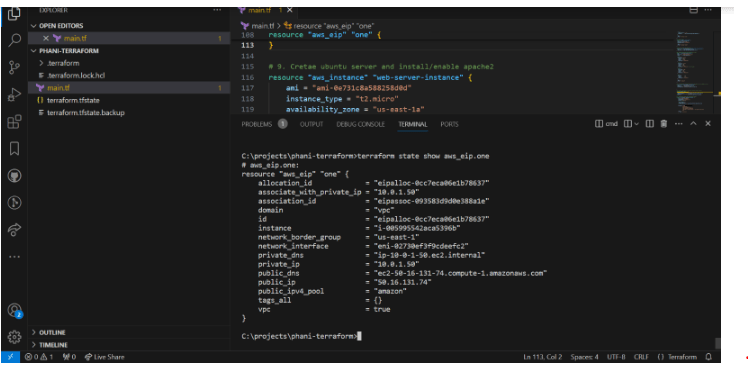
Now launch instance. And use key value pair to login to that instance
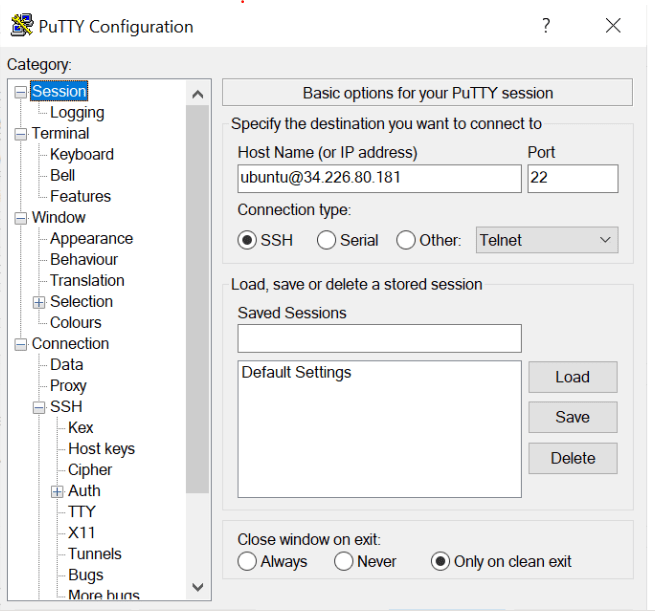
Now copy public ipv4 address shown in the pic.
Lets go to your terminal and get your keypair file name and ipv4 address.
ssh -i phani-keypair.pem ubuntu@54.196.110.205
You will see the below error when trying to connect to that instance
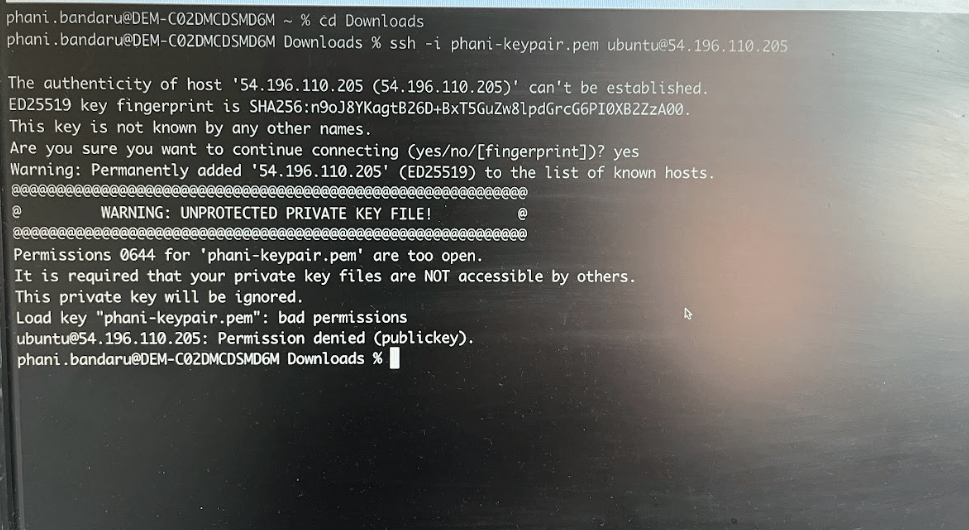
which means it is a very sensitive file which has lot of private key information
or sensitive information. you have to keep the permissions to open.
you can use a command called chmod to change the permissions of the file to 600
type in terminal chmod 600 phani-keypair.pem
Now I changed permission.
Now run ssh -i phani-keypair.pem ubuntu@54.196.110.205
Now I can log into ec2 instance
once you logged in, AWS will show you the private IP address of that server but you have logged in through the public IP address right so now you have technically inside the ec2 instance
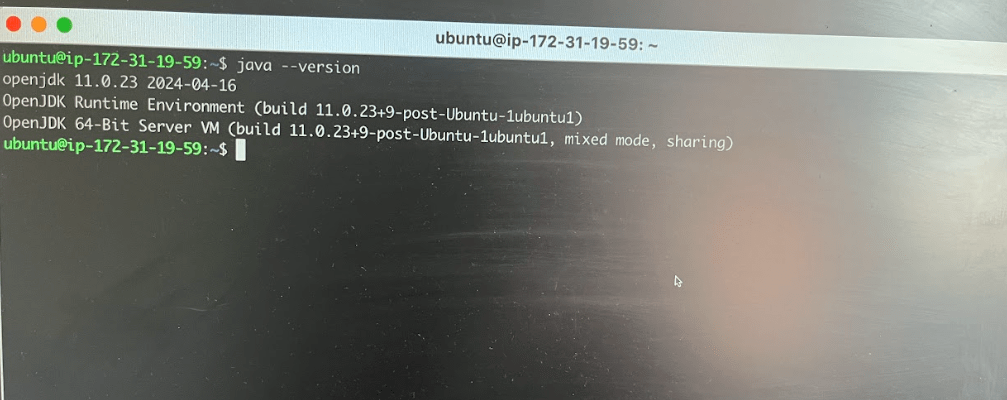
Now what you need to do is you have to update the packages on this instance
Sudo command is needed if you are on the Ubuntu
Now run below command to update pakcages
sudo apt update
Now let’s try to deploy an application
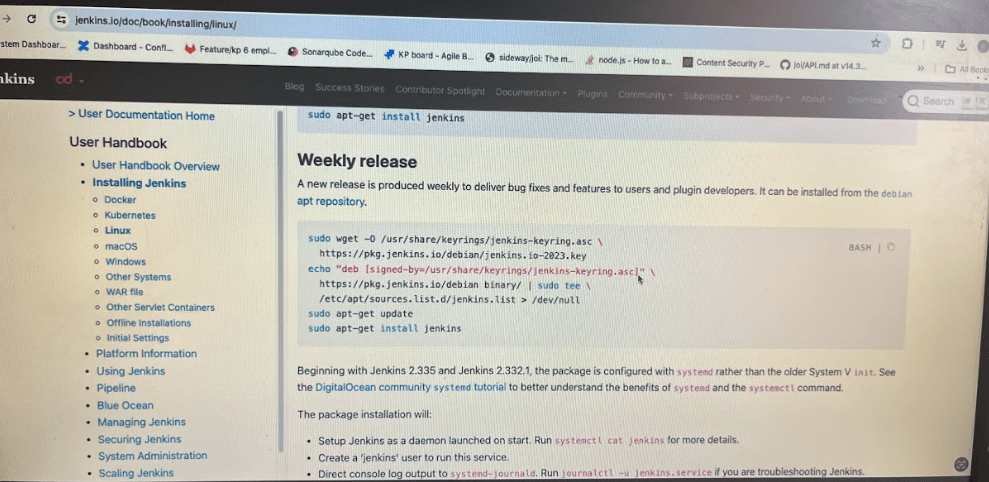
Lets install Jenkins on that ubuntu server
Preqrequisistes for Jenkins is to install java
So run the command
sudo apt install openjdk-11-jdk
Now install Jenkins. Its bit of commands to use. you can google it and can see in below image
we will start the Jenkins service if it is not started and once the Jenkins
service is started you can try to access it from the browser
Let’s see if jenkins server is running
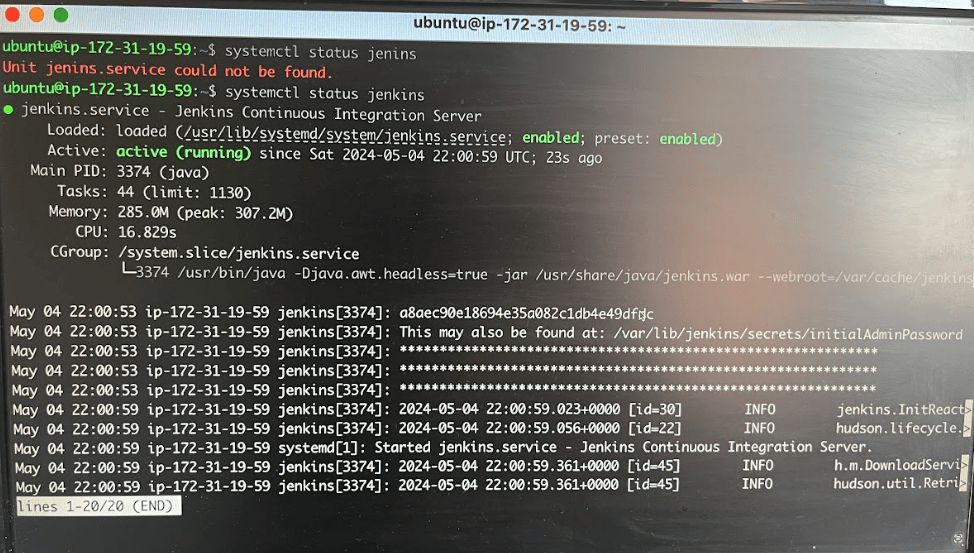
Use below command
systmectl status Jenkins
By default Jenkins runs on a port called 8080
Now go to browser and running http://publicipaddress:8080 . here ip address is 54.196.110.205
Now it don’t run
Now the instance is running . But your application by default it is not accessible to the external World there are lot of security and networking things that i will show you later.
Now i will show you how to open that port 8080 for now as shown below
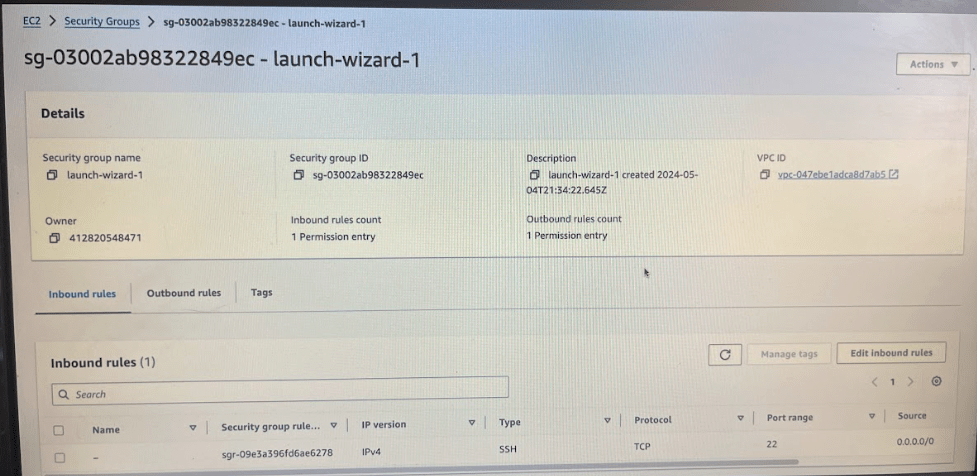
There is a security groups where it has inbound traffic rules and outbound traffic rules.
An inbound is a request which is coming inside AWS to your ec2 instance. An outbound is a request thats going outside
Go to the security group and Edit inbound rules.
Here I’ll edit the inbound traffic rules and I will tell that I will add a new rule saying that I allow custom TCP code 8080 from anywhere in the world I’ll just say anywhere ipv4 and I’ll just save the rule

Now go to browser and type http://54.196.110.205:8080/
You can see you are able to access Jenkins webpage

Hurray !!
We deployed our application to Jenkins on AWS and able to access it from outside world